The nucleolus (/ nj uː ˈ k l iː ə l ə s, ˌ nj uː k l i ˈ oʊ l ə s /; pl.: nucleoli /-l aɪ /) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes.The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell’s response to stress.
How to Draw an Animal Cell Diagram -Homework Help | DoodleDrawArt – YouTube
The nucleus is generally considered the control center of the cell because it stores all of the genetic instructions for manufacturing proteins. Interestingly, some cells in the body, such as muscle cells, contain more than one nucleus (Figure 2.4.2 2.4. 2 ), so they are referred to as multinucleated cells. Other cells, such as mammalian red

Source Image: knowledgeclass.blogspot.com
Download Image
nucleolus, spherical body within the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells, involved in the synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and the formation of ribosomes.Nucleoli appear shortly after mitosis and form around specific repeating chromosome regions, known as nucleolar organizing regions, within the nucleus. A single nucleus can house one to several nucleoli, depending on the organism and cell type.
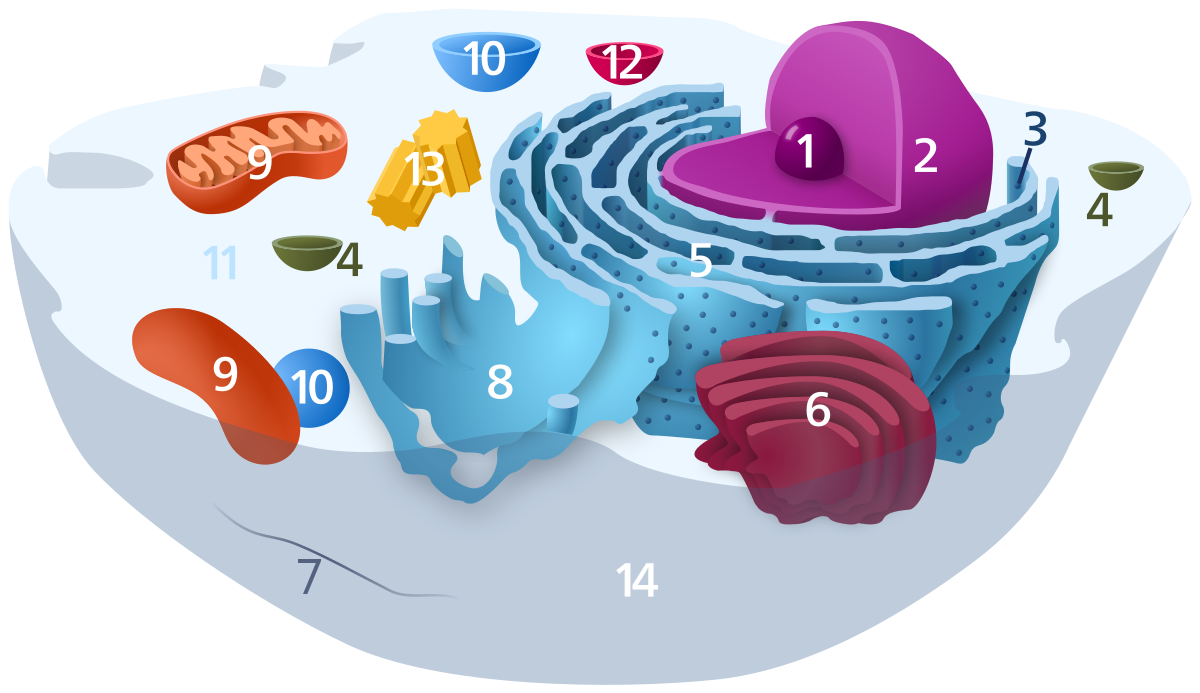
Source Image: en.wikipedia.org
Download Image
Animal Cell | by Biology Experts Notes | Medium The nucleolus, or plural nucleoli, is normally a circular structure composed of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleoli are not typical organelles for the reason that they have no lipid membrane, making it with of the few non-membrane bound organelles in the cell.

Source Image: apbionotebook.wordpress.com
Download Image
When Are The Nucleoli Visible What Organelles Are Assembled Here
The nucleolus, or plural nucleoli, is normally a circular structure composed of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleoli are not typical organelles for the reason that they have no lipid membrane, making it with of the few non-membrane bound organelles in the cell. The typical nucleus boasts 2-5 nucleoli, ranging in size from 0.5 to 5 μm in diameter. But many tumour cells have more and bigger NORs. And the more NORs, the worse the prognosis. So nucleoli could have a role in cancer. Anything else? Yes. Nucleoli may play a key role in the aging process.
Chapter 06: Tour of the Cell | AP Bio Notebook
Oct 30, 2023The nucleolus (plural: nucleoli) is a dark-staining, typically spherical body within the nucleus of a cell. It is a dense non-membrane-bound structure which forms a specialized subdomain of the nucleus that is responsible for the synthesis of ribosomal subunits.. Each nucleolus is composed of an aggregate of ribosomal genes, newly synthesized ribosomal RNA (rRNA), ribosomal proteins and cell organelles – BIOLOGY4ISC
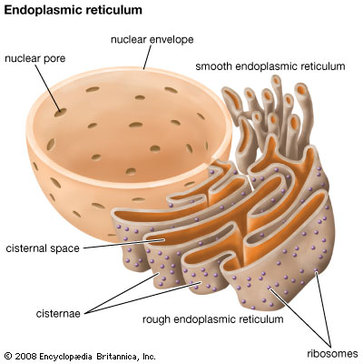
Source Image: biology4isc.weebly.com
Download Image
B for Biology: July 2013 Oct 30, 2023The nucleolus (plural: nucleoli) is a dark-staining, typically spherical body within the nucleus of a cell. It is a dense non-membrane-bound structure which forms a specialized subdomain of the nucleus that is responsible for the synthesis of ribosomal subunits.. Each nucleolus is composed of an aggregate of ribosomal genes, newly synthesized ribosomal RNA (rRNA), ribosomal proteins and
Source Image: namrataheda.blogspot.com
Download Image
How to Draw an Animal Cell Diagram -Homework Help | DoodleDrawArt – YouTube The nucleolus (/ nj uː ˈ k l iː ə l ə s, ˌ nj uː k l i ˈ oʊ l ə s /; pl.: nucleoli /-l aɪ /) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes.The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell’s response to stress.
Source Image: m.youtube.com
Download Image
Animal Cell | by Biology Experts Notes | Medium nucleolus, spherical body within the nucleus of most eukaryotic cells, involved in the synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and the formation of ribosomes.Nucleoli appear shortly after mitosis and form around specific repeating chromosome regions, known as nucleolar organizing regions, within the nucleus. A single nucleus can house one to several nucleoli, depending on the organism and cell type.
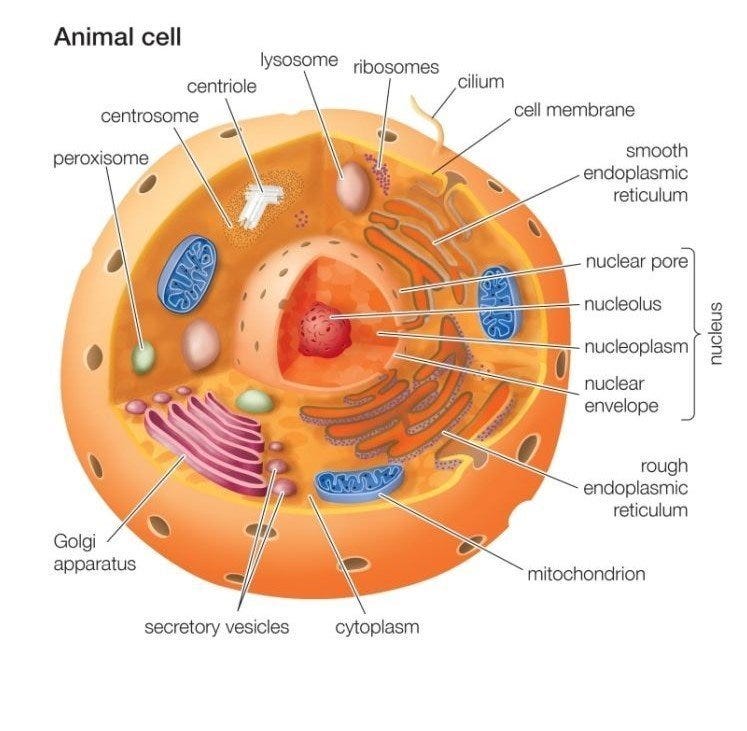
Source Image: medium.com
Download Image
Chapter 06: Tour of the Cell | AP Bio Notebook This is the nucleus of a cell in interphase (between cell divisions). A bluish purple line around the edge of the nucleus is the nuclear envelope/nuclear membrane. The small darkly staining granules are chromatin (chromosomes). The larger dark purple structure is the nucleolus. The nucleus of a cell in interphase.

Source Image: apbionotebook.wordpress.com
Download Image
Which cell organelle is called the head quarter of a cell? – Quora The nucleolus, or plural nucleoli, is normally a circular structure composed of proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleoli are not typical organelles for the reason that they have no lipid membrane, making it with of the few non-membrane bound organelles in the cell.
Source Image: quora.com
Download Image
Reimagining dots and dashes: Visualizing structure and function of organelles for high-content imaging analysis – ScienceDirect The typical nucleus boasts 2-5 nucleoli, ranging in size from 0.5 to 5 μm in diameter. But many tumour cells have more and bigger NORs. And the more NORs, the worse the prognosis. So nucleoli could have a role in cancer. Anything else? Yes. Nucleoli may play a key role in the aging process.

Source Image: sciencedirect.com
Download Image
B for Biology: July 2013
Reimagining dots and dashes: Visualizing structure and function of organelles for high-content imaging analysis – ScienceDirect The nucleus is generally considered the control center of the cell because it stores all of the genetic instructions for manufacturing proteins. Interestingly, some cells in the body, such as muscle cells, contain more than one nucleus (Figure 2.4.2 2.4. 2 ), so they are referred to as multinucleated cells. Other cells, such as mammalian red
Animal Cell | by Biology Experts Notes | Medium Which cell organelle is called the head quarter of a cell? – Quora This is the nucleus of a cell in interphase (between cell divisions). A bluish purple line around the edge of the nucleus is the nuclear envelope/nuclear membrane. The small darkly staining granules are chromatin (chromosomes). The larger dark purple structure is the nucleolus. The nucleus of a cell in interphase.