Step 1: Enter the formula for which you want to calculate the domain and range. The Domain and Range Calculator finds all possible x and y values for a given function. Step 2: Click the blue arrow to submit. Choose “Find the Domain and Range” from the topic selector and click to see the result in our Calculus Calculator ! Examples
Solved Determine the range of the following graph: 12 11 10 | Chegg.com
Mar 31, 20232. Set the denominator equal to zero for fractions with a variable in the denominator. When finding the domain of a fractional function, you must exclude all the x-values that make the denominator equal to zero, because you can never divide by zero. So, write the denominator as an equation and set it equal to 0.

Source Image: pearson.com
Download Image
Another way to identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs. Because the domain refers to the set of possible input values, the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x -axis. The range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the y -axis.
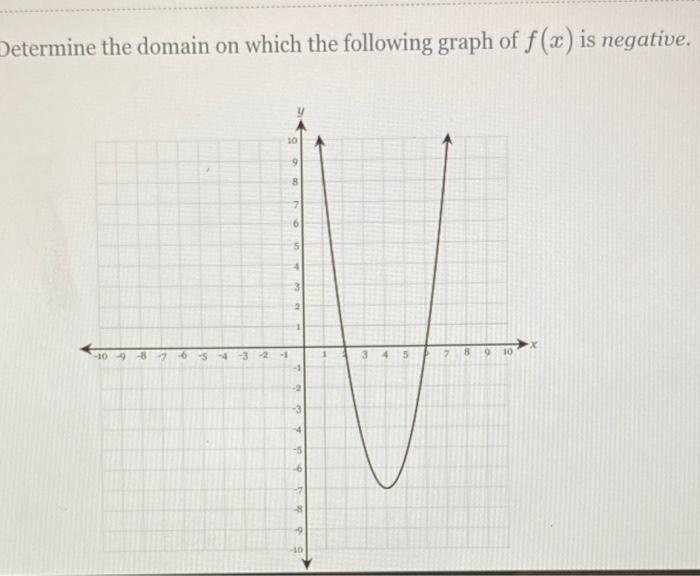
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
How to Find the Intercepts, Asymptotes, Domain, & Range from the Graph of a Rational Function | Precalculus | Study.com
The largest term in the interval is written second, following a comma. Parentheses, \((\) or \()\), are used to signify that an endpoint is not included, called exclusive. … Finding Domain and Range from a Graph. Find the domain and range of the function f whose graph is shown in Figure 1.2.8. Figure \(\PageIndex8\): Graph of a function

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Determine The Domain Of The Following Graph:
The largest term in the interval is written second, following a comma. Parentheses, \((\) or \()\), are used to signify that an endpoint is not included, called exclusive. … Finding Domain and Range from a Graph. Find the domain and range of the function f whose graph is shown in Figure 1.2.8. Figure \(\PageIndex8\): Graph of a function
AboutTranscript. Functions assign outputs to inputs. The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputs for the function. For example, the domain of f (x)=x² is all real numbers, and the domain of g (x)=1/x is all real numbers except for x=0. We can also define special functions whose domains are more limited.
How to Find the Domain and Range From the Graph of a Parabola | Algebra | Study.com
How to find domain and range from a graph (video) | Khan Academy Course: Algebra 1 > Unit 8 Lesson 5: Introduction to the domain and range of a function Intervals and interval notation What is the domain of a function? What is the range of a function? Worked example: domain and range from graph Domain and range from graph Math > Algebra 1 >
Finding Domain & Range from the Graph of a Continuous Function | Algebra | Study.com

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Determine Domain and Range from a Graph | College Algebra
How to find domain and range from a graph (video) | Khan Academy Course: Algebra 1 > Unit 8 Lesson 5: Introduction to the domain and range of a function Intervals and interval notation What is the domain of a function? What is the range of a function? Worked example: domain and range from graph Domain and range from graph Math > Algebra 1 >
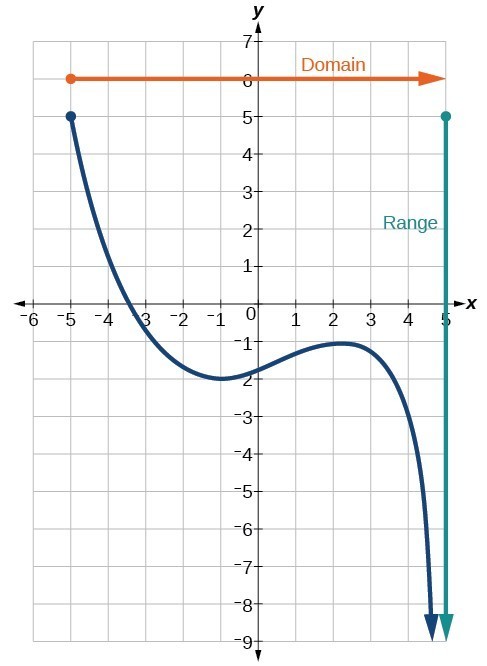
Source Image: courses.lumenlearning.com
Download Image
Solved Determine the range of the following graph: 12 11 10 | Chegg.com
Step 1: Enter the formula for which you want to calculate the domain and range. The Domain and Range Calculator finds all possible x and y values for a given function. Step 2: Click the blue arrow to submit. Choose “Find the Domain and Range” from the topic selector and click to see the result in our Calculus Calculator ! Examples
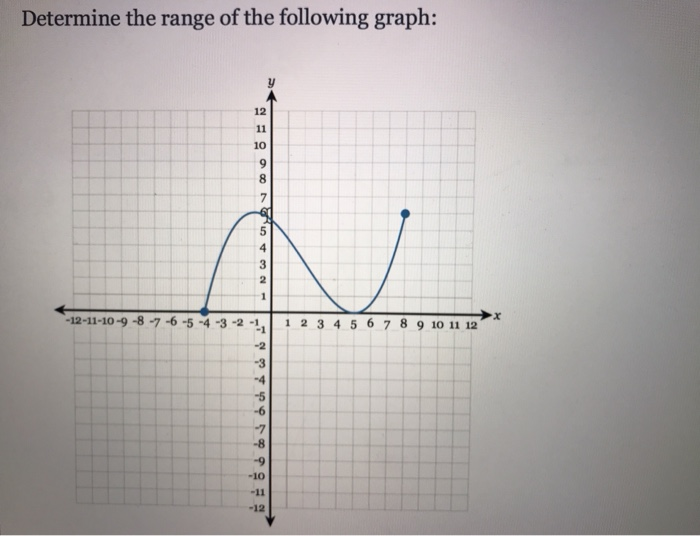
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
How to Find the Intercepts, Asymptotes, Domain, & Range from the Graph of a Rational Function | Precalculus | Study.com
Another way to identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs. Because the domain refers to the set of possible input values, the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the x -axis. The range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the y -axis.

Source Image: study.com
Download Image
Solved Determine the domain on which the following graph of | Chegg.com
For any real number, you can always find an x value that gives you that number for the output. Unless a linear function is a constant, such as f (x) = 2 f ( x) = 2, there is no restriction on the range. The domain and range are all real numbers. For the examples that follow, try to figure out the domain and range of the graphs before you look
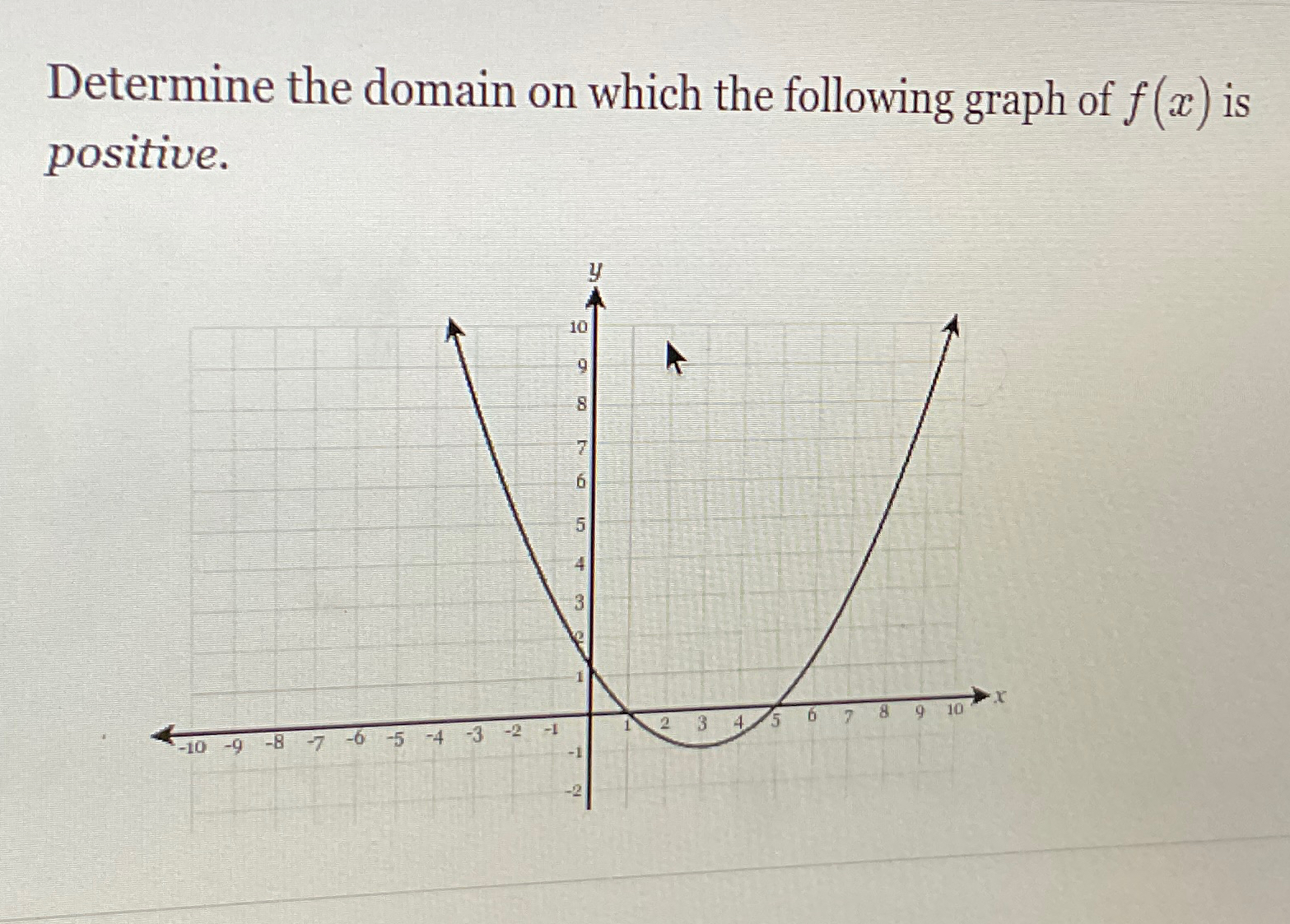
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Functions | PPT
The largest term in the interval is written second, following a comma. Parentheses, \((\) or \()\), are used to signify that an endpoint is not included, called exclusive. … Finding Domain and Range from a Graph. Find the domain and range of the function f whose graph is shown in Figure 1.2.8. Figure \(\PageIndex8\): Graph of a function

Source Image: slideshare.net
Download Image
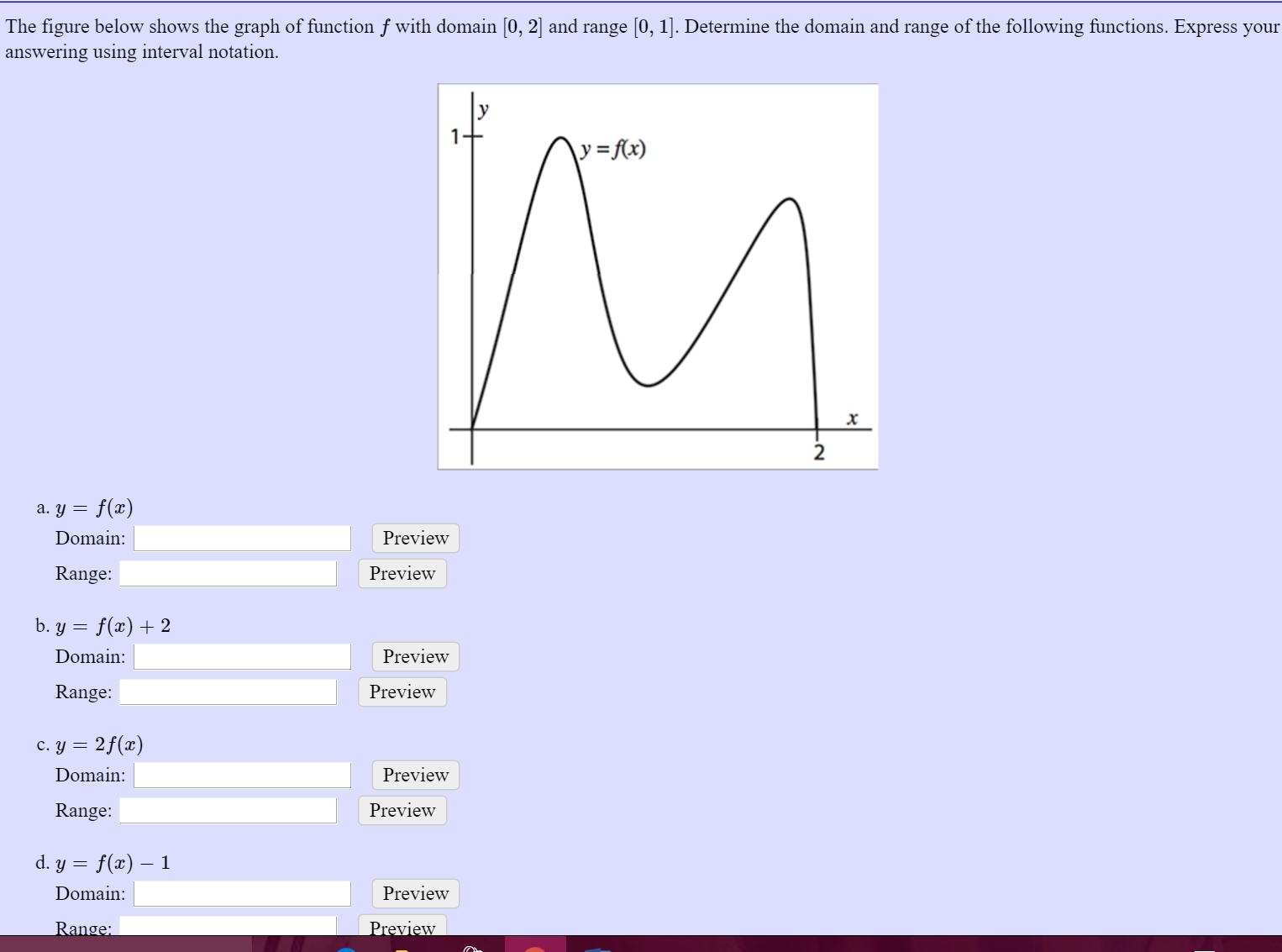
Solved The figure below shows the graph of function f with | Chegg.com
AboutTranscript. Functions assign outputs to inputs. The domain of a function is the set of all possible inputs for the function. For example, the domain of f (x)=x² is all real numbers, and the domain of g (x)=1/x is all real numbers except for x=0. We can also define special functions whose domains are more limited.
Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Determine Domain and Range from a Graph | College Algebra
Solved The figure below shows the graph of function f with | Chegg.com
Mar 31, 20232. Set the denominator equal to zero for fractions with a variable in the denominator. When finding the domain of a fractional function, you must exclude all the x-values that make the denominator equal to zero, because you can never divide by zero. So, write the denominator as an equation and set it equal to 0.
How to Find the Intercepts, Asymptotes, Domain, & Range from the Graph of a Rational Function | Precalculus | Study.com Functions | PPT
For any real number, you can always find an x value that gives you that number for the output. Unless a linear function is a constant, such as f (x) = 2 f ( x) = 2, there is no restriction on the range. The domain and range are all real numbers. For the examples that follow, try to figure out the domain and range of the graphs before you look